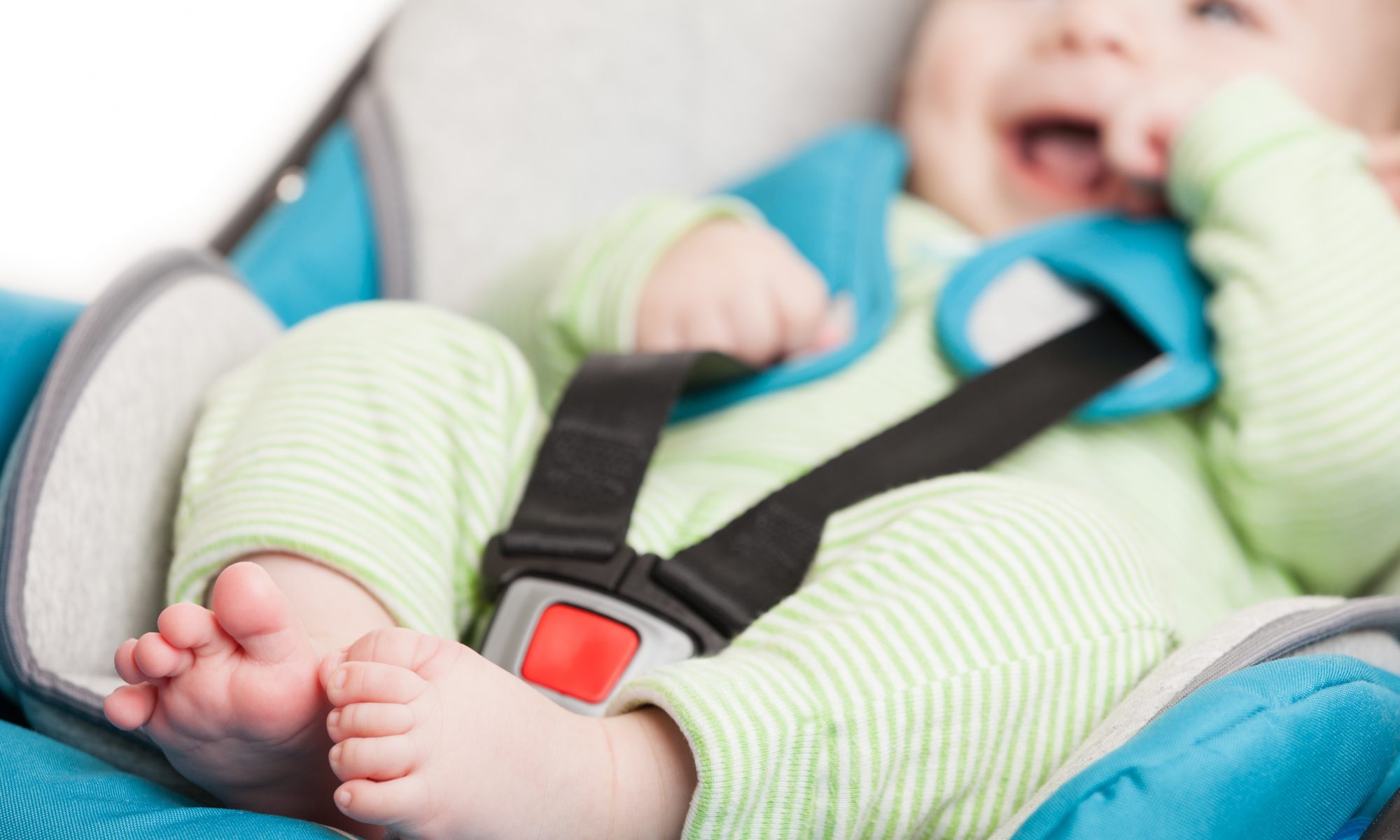
Babies sleep safest flat on their backs, in a crib or other safe sleep surface with a tightly fitted sheet. Car seats, strollers and swings all place babies in an upright position which, similar to sleeping on their tummies, puts them at risk for suffocation.
This illustration from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development helps illustrate how babies sleeping on their stomachs are at a higher risk for choking and suffocation.
When a baby sleeps on his or her stomach, fluids will exit the esophagus and pool at the opening of the trachea, making choking much more likely. Likewise, babies sleeping upright and on their sides are at a similar risk.
Experts recommend babies shouldn’t be allowed to sleep in car seats or similar devices like strollers and bouncers for an extended period of time (more than one to two hours, depending on the age of your baby and the device).
If you’re going on an extended car trip, experts suggest stopping at least every two hours and removing your infant from the car seat. Never leave a baby unattended in any device, especially newborns or babies under six months who can’t hold their heads up yet. It’s also important to always follow manufacturers’ recommendations for using a device, and pay attention to straps and harnesses.
If you have questions related to safe sleep, speak with your child’s medical provider or contact your local health department.